Purines are a type of chemical compound found in various foods and also produced naturally by the body. They play an important role in the synthesis of DNA, RNA and energy molecules such as ATP. People whose body maintains high levels of uric acid should be careful with the consumption of such products. The deposition of uric acid as crystals around the small joints causes a gout attack. It is painful and has the risk of long-term health effects.
Purines are broken down into uric acid in the body
When purines are broken down in the body, they produce a waste product called uric acid. It is usually dissolved in the blood and excreted from the body through the urine. However, in some people, the body produces large amounts of uric acid. There may be difficulty in effectively eliminating it through the urine. Either cause leads to a condition known as hyperuricemia.
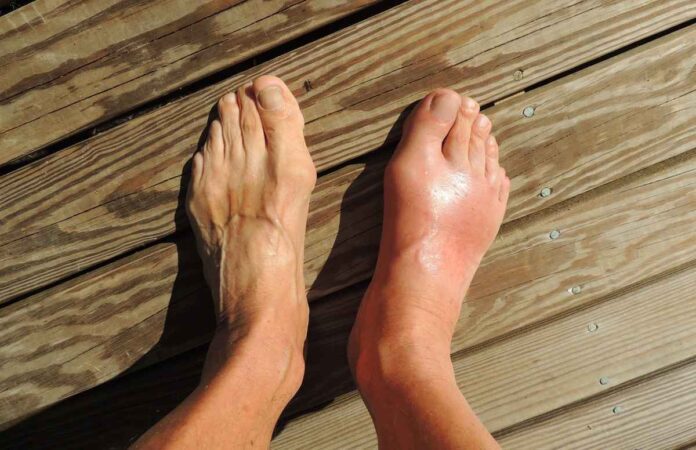
This condition can occur with or without symptoms. In some people, elevated laboratory values of uric acid are detected, but they do not have any complaints, they do not feel anything. Others have symptoms. A typical gout attack is associated with sudden pain in the big toe that often occurs at night. In the morning, a person may think that he has hit something without remembering. The pain is sharp, stabbing. Symptoms may also appear in other joints.
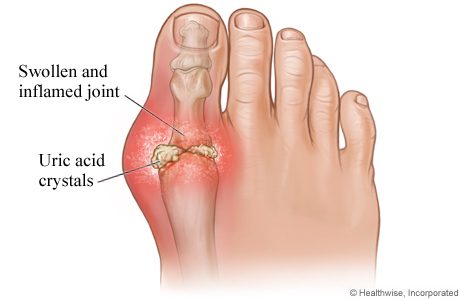
Gout is a form of arthritis that is directly related to elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. When uric acid levels become too high, it crystallizes and deposits in the joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues. This leads to inflammation and severe pain. The big toe is usually affected, but gout can also affect other joints such as the ankles, knees, wrists and fingers.
Gout often develops in the context of metabolic syndrome. Abdominal fattening, blood sugar and blood pressure are elevated. There may also be dyslipidaemia – high levels of fat in the blood (triglycerides, cholesterol).
Foods rich in purines - why diet is important
Dietary intake of purine-rich foods can contribute to increased levels of uric acid in the body. Foods high in purines include organ meats (such as liver and kidney), seafood (such as anchovies, sardines, and scallops), red meat, some vegetables (such as spinach, mushrooms, and cauliflower), and certain beverages (such as beer and sweetened drinks). However, it is important to note that dietary purines contribute only a small portion of total uric acid levels, as most uric acid is produced internally by the body.

In addition to diet, other factors that can contribute to gout include genetics, obesity, certain medications (such as diuretics), underlying medical conditions (such as kidney disease), and excessive alcohol consumption.
Treatment for gout usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. This may include reducing the intake of purine-rich foods, maintaining a healthy weight, drinking enough water (to flush out as many metabolites as possible through the urine), limiting alcohol consumption.
In many cases, medication must be taken to lower uric acid levels as well as for pain during gout attacks. There are different types of medications that help eliminate uric acid through the kidneys. This therapy is important because high levels of hyperuricemia pose a long-term risk to the heart and blood vessels. Without treatment, atherosclerosis progresses very quickly.
If you suspect you have gout or have symptoms, it is advisable to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Specialists who can treat this disease are endocrinologists, cardiologists or rheumatologists.
What products, foods contain purines?

Here are some examples of foods that contain different levels of purines:
Foods with a high purine content (more than 200 mg per 100 grams)
- Organic meats (liver, kidney, sweetbreads)
- Game meat (venison, rabbit)
- Anchovies, sardines and other oily fish
- Clams, clams and more clams
- Sauce and meat broth
- Foods with a moderate purine content (between 100-200 mg per 100 grams):
- Red meats (beef, pork, lamb)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Fish (excluding oily fish mentioned above)
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans)
- Mushrooms, spinach, asparagus, cauliflower
- Yeast extracts (Marmite, Vegemite)
Foods with a low purine content (less than 100 mg per 100 grams):
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
- Eggs
- Fruits and vegetables (except those mentioned above)
- Cereals (rice, bread, pasta)
- Nuts and seeds
It is important to note that the purine content of certain foods can vary and these values are approximate. Additionally, dietary purines contribute only a small fraction of total uric acid levels in the body. Most uric acid is produced internally.
Editor Ina Dimitrova