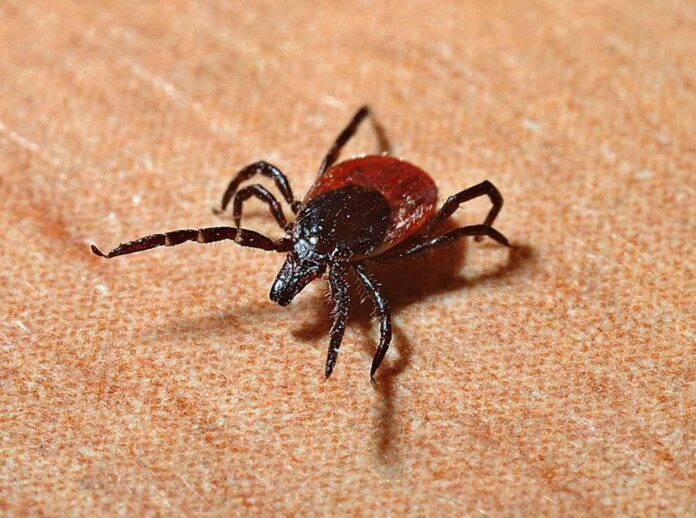
Lyme disease is usually treated with antibiotics. The most effective types of antibiotics in this case target the bacterium that causes the infection, which is called Borrelia burgdorferi. The choice of antibiotics and duration of treatment depend on the stage of Lyme disease, the severity of symptoms, and any possible complications. The instructions below are for informational purposes only and should not be used for self-medication. Antibiotics are prescribed by a doctor with instructions for the exact dose and duration of treatment.
Lyme disease symptoms and diagnosis
Lyme disease is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and laboratory testing. Here is an overview of the diagnostic process:
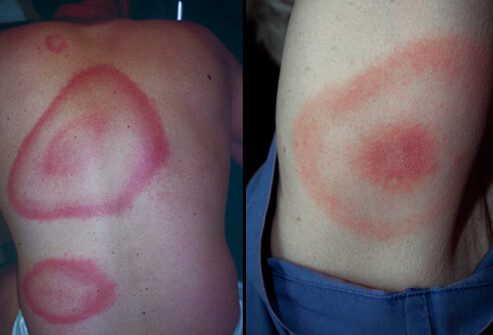
The characteristic symptom of Lyme disease is a circular rash known as erythema migrans (pictured below), but not all people develop this rash. Other symptoms may include fever, fatigue, headache, muscle and joint pain, and swollen lymph nodes.
Laboratory researches:
Serological testing: Blood tests are usually used to detect antibodies produced by the immune system in response to Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria that causes Lyme disease. The two main types of serological tests are enzyme immunoassay (EIA) and Western blot. These tests are performed to confirm the presence of antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): In certain cases, a PCR test can be used to detect Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in blood, joint fluid, or tissue samples. The PCR test is most useful in the early stages of the disease, when the bacteria may be present in the bloodstream.
It is important to note that the accuracy of diagnostic tests can vary depending on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, the probability of getting a positive test result is less because of the time it takes immune system to produce detectable levels of antibodies. For this reason, clinical assessment and history are crucial for diagnosis.
On the other hand, you should not delay seeing a doctor, even if you do not have very pronounced symptoms. Early detection and treatment are important for effective treatment.
Which antibiotics are the most effective treatments for Lyme disease
Here are some commonly prescribed antibiotics for Lyme disease—they are sold under different brand names in pharmacies:
Doxycycline: This is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic for early stage Lyme disease. It is effective against Borrelia burgdorferi and is usually taken orally for 10 to 21 days. Doxycycline is not recommended for use in pregnant women and young children.
Amoxicillin, cefuroxime, or ceftriaxone: These antibiotics are often prescribed to patients who cannot take doxycycline, such as pregnant women and young children. These are usually used for early stage Lyme disease and can be taken by mouth or given intravenously in more severe cases.
Ceftriaxone: This antibiotic is often used in the treatment of late-stage or disseminated Lyme disease, where the infection has spread to multiple organs or the nervous system. It is administered intravenously for a period of 14 to 28 days.
It is important to note that these are general guidelines and treatment plans should be tailored to the individual patient's needs. If you suspect you have or have been diagnosed with Lyme disease, see a doctor.
How long does antibiotic treatment last for Lyme disease?

The length of antibiotic treatment for Lyme disease can vary depending on several factors, including the stage of the disease and the severity of symptoms. Generally, the recommended duration of treatment for Lyme disease is as follows:
Early localized Lyme disease (as a localized rash known as erythema migrans): The standard treatment is usually a course of oral antibiotics for 10 to 21 days. During this stage, doxycycline, amoxicillin or cefuroxime axetil are usually prescribed.
Early disseminated Lyme disease (when the infection has spread beyond the site of tick bite, but has not yet affected the central nervous system): Treatment usually involves oral antibiotics for 14 to 21 days. Doxycycline, amoxicillin or cefuroxime axetil may be prescribed.
Late-stage Lyme disease (when the infection has spread to the central nervous system, joints, or other organs): Intravenous (IV) antibiotics are often used for a longer period, usually ranging from 14 to 28 days. Ceftriaxone is usually given by IV for this stage.
It is important to remember that these are general guidelines and treatment decisions should be made by a healthcare professional based on individual patient factors. The duration of antibiotic treatment may be adjusted depending on the patient's response to treatment. It also depends on the presence of complications or concomitant infections. Regular follow-up with a health care provider is essential to ensure appropriate management of Lyme disease.
Can Lyme disease be completely cured with antibiotics?

In general, Lyme disease can be effectively treated with appropriate antibiotic therapy, especially if diagnosed and treated early. Most people with Lyme disease recover completely or experience significant improvement after completing the recommended course of antibiotics. However, in some cases, full recovery may take longer. Especially when the disease has progressed to the later stages or when there are complications. Some symptoms may persist even after treatment.
It is important to note that there is a small percentage of people who may experience what is known as post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS). PTLDS refers to the persistence of symptoms. These are fatigue, muscle and joint pain, and difficulty concentrating, despite completion of appropriate antibiotic treatment. The exact cause of PTLDS is not yet fully understood. It is thought to involve a combination of factors – persistent inflammation and immune system responses.
If you have been treated for Lyme disease but continue to experience persistent or recurring symptoms, see a doctor. He will recommend tests and treatment.
Early detection, prompt treatment, and compliance with the prescribed antibiotic regimen are essential to increase the chances of a full recovery from Lyme disease.
Author Ina Dimitrova


